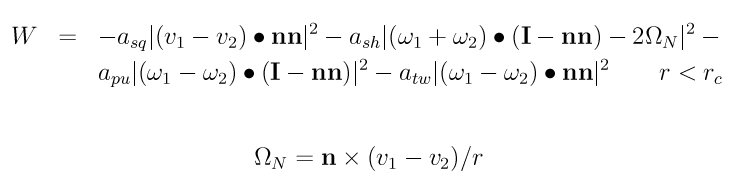
Syntax:
pair_style style mu flaglog flagfld cutinner cutoff
Examples: (all assume radius = 1)
pair_style lubricate 1.5 1 1 2.01 2.5 pair_coeff 1 1 2.05 2.8 pair_coeff * *
pair_style lubricate 1.5 1 1 2.01 2.5 pair_coeff * * variable mu equal ramp(1,2) fix 1 all adapt 1 pair lubricate mu * * v_mu
Description:
Styles lubricate and lubricate/poly compute hydrodynamic interactions between mono-disperse spherical particles in a pairwise fashion. The interactions have 2 components. The first is Ball-Melrose lubrication terms via the formulas in (Ball and Melrose)
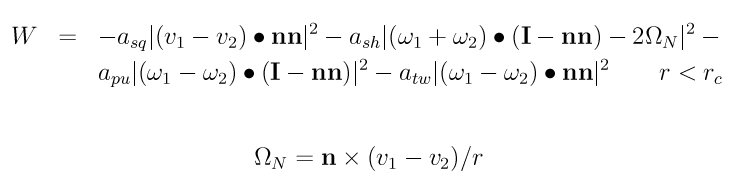
which represents the dissipation W between two nearby particles due to their relative velocities in the presence of a background solvent with viscosity mu. Note that this is dynamic viscosity which has units of mass/distance/time, not kinematic viscosity.
The Asq (squeeze) term is the strongest and is always included. It scales as 1/gap where gap is the separation between the surfaces of the 2 particles. The Ash (shear) and Apu (pump) terms are only include if flaglog is set to 1. Thy are the next strongest interactions, and the only other singular interaction, and scale as log(gap). The Atw (twist) term is currently not included. It is typically a very small contribution to the lubrication forces.
Cutinner sets the minimum center-to-center separation that will be used in calculations irrespective of the actual separation. Cutoff is the maximum center-to-center separation at which an interaction is computed. Using a cutoff less than 3 radii is recommended if flaglog is set to 1.
The other component is due to the Fast Lubrication Dynamics (FLD) approximation, described in (Kumar), which can be represented by the following equation
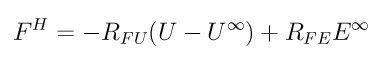
where U represents the velocities and angular velocities of the particles, U^infty represents the velocity and the angular velocity of the undisturbed fluid, and E^infty represents the rate of strain tensor of the undisturbed fluid with viscosity mu. Again, note that this is dynamic viscosity which has units of mass/distance/time, not kinematic viscosity.
IMPORTANT NOTE: When using the FLD terms, these pair styles are designed to be used with explicit time integration and a correspondingly small timestep. Thus either fix nve/sphere or fix nve/asphere should be used for time integration. To perform implicit FLD, see the pair_style lubricateU command.
Style lubricate requires monodisperse spherical particles; style lubricate/poly allows for polydisperse spherical particles.
The viscosity mu can be varied in a time-dependent manner over the course of a simluation, in which case in which case the pair_style setting for mu will be overridden. See the fix adapt command for details.
If the suspension is sheared via the fix deform command then the pair style uses the shear rate to adjust the hydrodynamic interactions accordingly.
Since lubrication forces are dissipative, it is usually desirable to thermostat the system at a constant temperature. If Brownian motion (at a constant temperature) is desired, it can be set using the pair_style brownian command. These pair styles and the brownian style should use consistent parameters for mu, flaglog, flagfld, cutinner, and cutoff.
The following coefficients must be defined for each pair of atoms types via the pair_coeff command as in the examples above, or in the data file or restart files read by the read_data or read_restart commands, or by mixing as described below:
The two coefficients are optional. If neither is specified, the two cutoffs specified in the pair_style command are used. Otherwise both must be specified.
Styles with a cuda, gpu, omp, or opt suffix are functionally the same as the corresponding style without the suffix. They have been optimized to run faster, depending on your available hardware, as discussed in this section of the manual. The accelerated styles take the same arguments and should produce the same results, except for round-off and precision issues.
These accelerated styles are part of the USER-CUDA, GPU, USER-OMP and OPT packages, respectively. They are only enabled if LAMMPS was built with those packages. See the Making LAMMPS section for more info.
You can specify the accelerated styles explicitly in your input script by including their suffix, or you can use the -suffix command-line switch when you invoke LAMMPS, or you can use the suffix command in your input script.
See this section of the manual for more instructions on how to use the accelerated styles effectively.
Mixing, shift, table, tail correction, restart, rRESPA info:
For atom type pairs I,J and I != J, the two cutoff distances for this pair style can be mixed. The default mix value is geometric. See the "pair_modify" command for details.
This pair style does not support the pair_modify shift option for the energy of the pair interaction.
The pair_modify table option is not relevant for this pair style.
This pair style does not support the pair_modify tail option for adding long-range tail corrections to energy and pressure.
This pair style writes its information to binary restart files, so pair_style and pair_coeff commands do not need to be specified in an input script that reads a restart file.
This pair style can only be used via the pair keyword of the run_style respa command. It does not support the inner, middle, outer keywords.
Restrictions:
These styles are part of the FLD package. They are only enabled if LAMMPS was built with that package. See the Making LAMMPS section for more info.
Only spherical monodisperse particles are allowed for pair_style lubricate.
Only spherical particles are allowed for pair_style lubricate/poly.
Related commands:
pair_coeff, pair_style lubricateU
Default: none
(Ball) Ball and Melrose, Physica A, 247, 444-472 (1997).
(Kumar) Kumar and Higdon, Phys Rev E, 82, 051401 (2010).